Proper wound care is crucial for ensuring optimal healing and preventing complications. Whether you have a minor cut or a more severe injury, knowing how to care for your wound can make a significant difference in the recovery process. In this blog post, we will guide you through essential steps and best practices to promote effective wound healing and minimize the risk of infections.
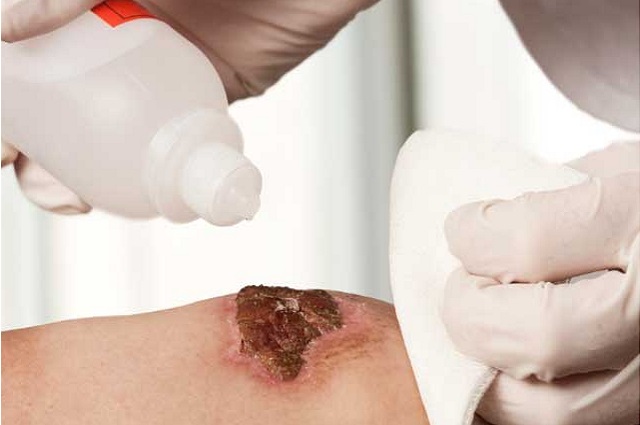
Cleanse the Wound:
The first step in proper wound care is to cleanse the affected area. Start by washing your hands thoroughly with soap and water. Gently clean the wound using mild soap and lukewarm water or a sterile saline solution. Avoid using hydrogen peroxide or alcohol, as they can damage healthy tissue. Pat the area dry with a clean, sterile towel or allow it to air dry naturally.
Apply an Appropriate Dressing:
Selecting the right dressing plays a vital role in wound healing. For minor cuts and scrapes, a simple adhesive bandage or sterile gauze pad may suffice. For larger or more complex wounds, consult a healthcare professional for guidance. The dressing should keep the wound clean, maintain a moist environment, and protect it from external contaminants. Change the dressing regularly as directed by your healthcare provider and ensure you have a fresh supply of sterile dressings on hand.
Manage Exudate:
Exudate refers to the fluid that oozes from the wound during the healing process. It is essential to monitor the amount and consistency of exudate. Excessive or foul-smelling exudate may indicate infection or other complications. Consult your healthcare provider if you notice any abnormal changes. In some cases, additional absorptive dressings or negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) may be recommended to manage excessive exudate.
Promote Moist Wound Healing:
Contrary to popular belief, keeping a wound moist promotes faster healing. Moist wound healing creates an optimal environment for cell regeneration and minimizes scarring. Moisturizing dressings, hydrogels, or saline-soaked dressings can help maintain a moist environment. However, remember that excessive moisture can lead to maceration, so strike a balance. Consult your healthcare provider for specific recommendations on the best approach for your wound.
Prevent Infections:
Preventing infections is crucial in wound care. Keep an eye out for signs of infection, such as increased pain, redness, swelling, warmth, or the presence of pus. To reduce the risk of infection, clean the wound regularly, apply appropriate antimicrobial dressings if recommended, and avoid touching the wound with dirty hands. Additionally, ensure your tetanus vaccination is up to date, particularly for deeper or contaminated wounds. If you suspect an infection, seek medical attention promptly.
Support Overall Healing:
A healthy lifestyle can contribute to faster wound healing. Eat a balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and protein to provide your body with the necessary building blocks for tissue repair. Avoid smoking, as it impairs blood circulation and delays healing. Get sufficient rest and manage stress, as these factors can impact the body's ability to heal. Follow any specific instructions provided by your healthcare provider regarding wound care, medications, and activity restrictions.
Proper wound care is a fundamental aspect of recovery. By following these essential steps, you can promote optimal healing, reduce the risk of complications, and facilitate a smoother healing process. Remember, if you have any concerns or questions about wound care, consult a healthcare professional for guidance and support.

